Access the complete WAEC Geography Answers for 2025 here. This page will be updated with verified solutions to both Objective (OBJ) and Essay questions before the exam begins. Be sure to refresh this page regularly for the latest updates and accurate answers as they become available.
WAEC GEOGRAPHY LANGUAGE OBJ 2025
01-10: CBACBBBCCB
11-20: ABBDACCDBA
21-30: BBDCCCBADA
31-40: BABDABDBDA
41-50: CACACCACBD
COMPLETED!!
WAEC GEOGRAPHY LANGUAGE Essay 2025
Number 1
(1a)
(i)Rapid population growth: Developing countries often experience high rates of urbanization as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of opportunities.
(ii)Informal settlements:
Due to rapid urbanization and lack of affordable housing, many urban areas in developing countries have a significant presence of informal settlements or slums.
(iii)Inadequate infrastructure: Urban areas in developing countries often struggle with inadequate infrastructure, including limited access to clean water, sanitation, electricity, and transportation.
(iv)High levels of unemployment and
poverty: Despite the opportunities that cities offer, many urban residents in developing countries face high levels of unemployment and poverty.
(v)Social and economic
inequalities: Urban areas in developing countries often exhibit significant social and economic inequalities, with disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and services.
(1b)
(i)Food supply: Urban areas depend on rural settlements for their food supply, as rural areas are often the primary producers of agricultural products.
(ii)Labor force: Rural areas often provide a labor force for urban industries and services, as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of employment.
(iii)Natural resources: Urban areas depend on rural areas for natural resources, such as water, timber, and minerals.
(iv)Recreation and tourism: Rural areas often provide recreational and tourist opportunities for urban residents, offering a break from the hustle and bustle of city life.
Cultural and social
(v)connections: Urban areas often maintain cultural and social connections with surrounding rural areas, as many urban residents have family and cultural ties to rural communitie
==================
Number 2
(2a)
The balance of trade is the difference between a country’s total value of exports and its total value of imports over a specific period.
(2b)
(i)Demand for raw materials: Developed countries often require raw materials and agricultural products that are abundant in Tropical Africa.
(ii)Demand for manufactured goods: Tropical African countries often need manufactured goods and technologies that are produced in developed countries.
(iii)Investment: Foreign direct investment from developed countries can help boost production and trade in Tropical Africa.
(iv)Trade agreements: Trade agreements between Tropical African countries and developed countries can reduce trade barriers and promote trade.
(v)Transportation: Improvements in transportation infrastructure, such as ports and roads, can facilitate trade.
(2c)
(i)Increased economic growth: Trade can increase economic growth by allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage.
(ii)Access to new markets: International trade provides access to new markets for Tropical African products, which can lead to increased sales and revenue.
(iii)Access to technology: International trade can provide access to new technologies and know-how, which can help to improve productivity and efficiency.
(iv)Job creation: International trade can create new jobs in export-oriented industries.
==================
Number 3
(3a)
Pipeline transportation is the method of transporting liquids and gases through a system of pipes from one location to another.
(3b)
(i) Crude oil
(ii) Natural gas
(3ci)
(i)Cost-Effective: Pipelines are a cost-effective way to transport large volumes of liquids and gases over long distances, reducing transportation costs compared to other methods.
(ii)Continuous Supply: Pipelines provide a continuous and reliable supply of resources, ensuring a steady flow of materials like oil and gas.
(iii)Environmentally Friendly: Compared to other modes like rail and oil ships, pipelines have a reduced environmental impact, especially when buried underground.
(iv)Reduced Traffic Congestion: Pipelines can help alleviate traffic congestion by reducing the need for trucks and other vehicles to transport goods.
(3cii)
(i)Vandalism and Theft: Pipelines are susceptible to vandalism and theft, which can lead to leaks, environmental damage, and economic losses.
(ii)High Initial Costs: Building pipelines requires significant upfront investment, which can be a barrier to development, especially in countries with limited resources.
(iii)Land Acquisition Challenges: Constructing pipelines often involves acquiring land, which can be difficult and lead to conflicts with local communities.
(iv)Maintenance and Repair: Pipelines require regular maintenance and repair, and failures can lead to disruptions in supply and environmental contamination.
Number 4
(4a)
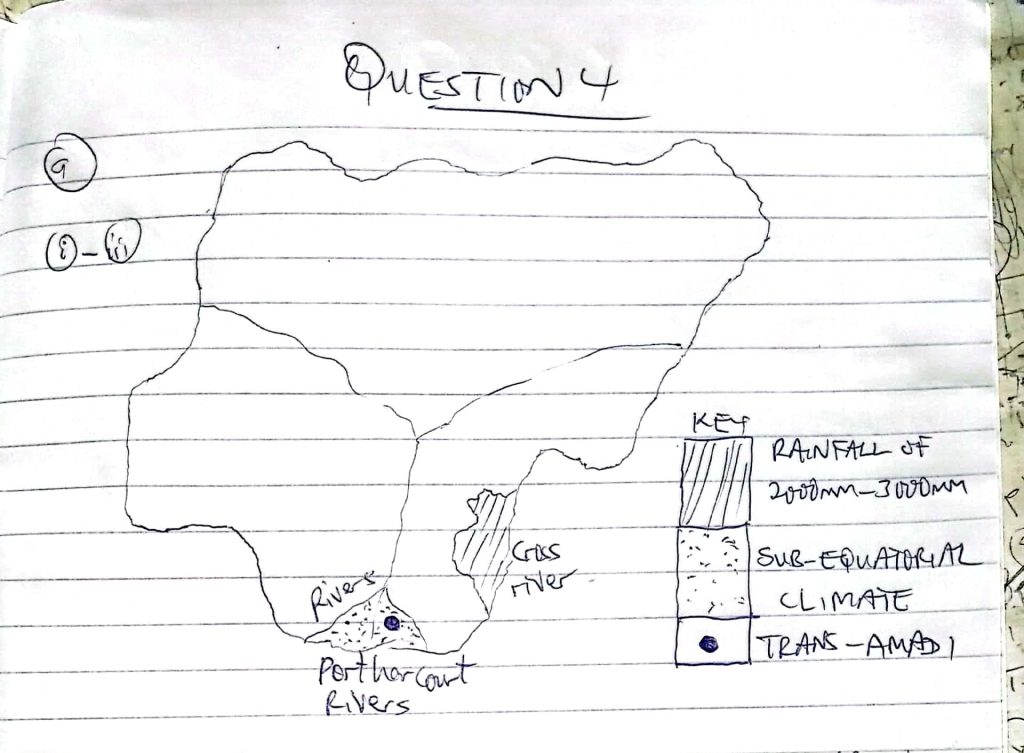
(4b)
(i)Latitude: Areas closer to the equator generally receive more rainfall than those further away.
(ii)Prevailing Winds: The direction and moisture content of winds influence rainfall patterns.
(iii)Altitude: Higher elevations tend to receive more rainfall than low-lying areas.
(iv)Distance from the Coast: Coastal regions receive more rainfall compared to inland areas.
(4c)
(i)High Rainfall: Sub-equatorial regions experience high annual rainfall, often exceeding 1500 mm.
(ii)High Temperatures: Temperatures are consistently high throughout the year.
(iii)Short Dry Season: The dry season is relatively short and less intense compared to other parts of Nigeria
==================
Number 5
(5a)
(i)Suitable Climate: Nigeria has a tropical climate with high rainfall and temperatures, ideal for cocoa growth.
(ii)Fertile Soil: The country has areas with well-drained, fertile soil that supports cocoa cultivation.
(iii)Traditional Farming Knowledge: Many farmers possess traditional knowledge of cocoa farming practices.
(iv) Government Support: Government initiatives, such as subsidies and training programs, encourage cocoa farming.
(v)Market Demand: Both local and international demand for cocoa beans provides an incentive for farmers to cultivate cocoa.
(5b)
(i)Pest and Disease Control: Implementing effective pest and disease management strategies can reduce crop losses.
(ii)Improved Farming Techniques: Training farmers on modern farming techniques, such as pruning and fertilization, can increase yields.
(iii)Access to Credit:
Providing farmers with access to loans and financial assistance can help them invest in their farms.
(iv)Infrastructure Development: Improving transportation infrastructure can facilitate the movement of cocoa beans to markets.
(v)Research and Development: Investing in research to develop high-yielding and disease-resistant cocoa varieties can boost production.
Number 6

